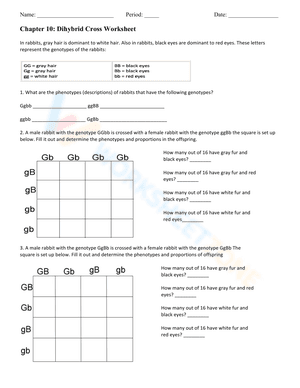
With 9th Grade Dihybrid Cross Worksheets PDF, engaging practice is always within reach, no matter your schedule or setting. Designed for early learners through middle grades, these 9th Grade Dihybrid Cross Worksheets PDF deliver high-impact worksheets that support key milestones and curriculum objectives. Each resource is professionally formatted for clarity, consistency, and ease of use, saving educators and parents hours of prep time. Forget the frustration of scattered, low-quality materials; 9th Grade Dihybrid Cross Worksheets PDF give you a cohesive collection that reinforces learning while building student confidence. Whether used for daily review, skill reinforcement, or enrichment, these worksheets make it easier to plan with purpose and teach with confidence. Elevate your instruction with targeted, ready-to-go resources that align with real learning needs.
More additional 9th Grade Human body system worksheets
More additional 9th Grade Human body system worksheets