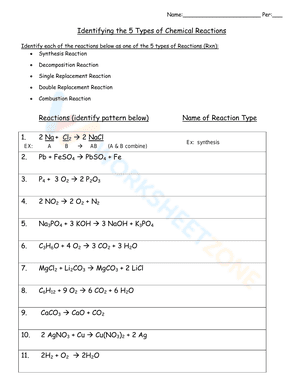
Gain instant access to 7th Grade Science Worksheets, a trusted resource for educators and families alike. Whether you're managing a full classroom or guiding at-home learning, these 7th Grade Science Worksheets offer structured, easy-to-follow worksheets that promote clear skill progression. Each sheet is organized by grade level and learning target, making it simple to find exactly what you need—no more wasting time on inconsistent online freebies. With built-in answer keys and enrichment prompts, these materials support effective instruction and confident learning. 7th Grade Science Worksheets empowers you to deliver smart, focused practice that meets students where they are and helps them grow. Save time, reduce stress, and prioritize what matters most: meaningful progress and student success.
More additional 7th Grade worksheets
More additional 7th Grade worksheets